We’ve had a great weekend! The pledges have kept coming in steadily and now we have passed the halfway mark and we are at 58% of our goal! We were also very excited to be featured in Atmel’s blog as I mentioned in the last post.
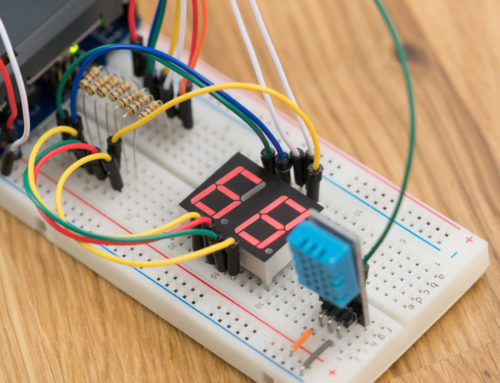
Several times I have made mention of the fuel gauge IC that is on the energyShield. It communicates via I2C (TWI) and measures voltage, current, and accumulated current (charge). You already knew that much, but I have never actually showed it in operation. Here are a couple of pictures that I snapped back in December.
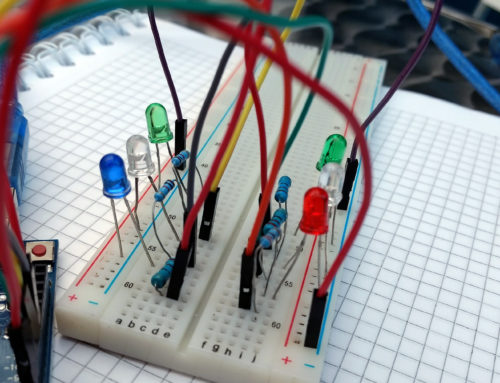
In this picture, and the one below, I have a simple project running on the Arduino that reads the fuel gauge and then outputs the reading on the LCD. Here I put load on the energyShield by wiring up some LEDs and a couple of 150 ohm resistors from + to -. The left side of the LCD shows the battery voltage (top) and the accumulated current (bottom). The full battery capacity was around 1300mAh so it only has about 18% charge left at this point. The right side of the LCD displays the current output at 5V (top) and the current output from the battery (pre-boost, bottom). As stated in the technical area, the current from the battery will be higher than the current output at 5V (P = V(bat)*I(bat)*efficiency = 5V*I(output). That this point in my testing I had not taken the efficiency into account. The efficiency is roughly 83%. That would make the actual current output at 5V around 183 mA.
In the second picture here, the current to the battery is negative because the energyShield is charging.
This just gives you a basic idea of what the energyShield’s fuel gauge is capable of. I have checked the reading of the fuel gauge against my multimeter and they are right on target. The energyShield library will also include a % remaining function. If you have any questions (please have some questions :D ) leave a comment here.
Thank you again for your support!




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.